 This tutorial provides an explanation of randomization in statistics, including a definition and several examples.
This tutorial provides an explanation of randomization in statistics, including a definition and several examples.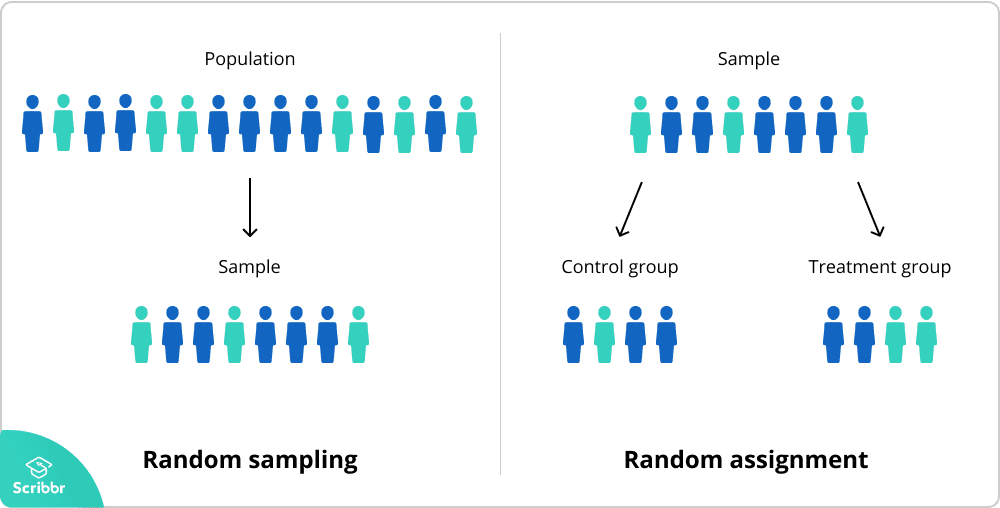 In experimental research, random assignment is a way of placing participants from your sample into different treatment groups using randomization. With simple random assignment, every member of the sample has a known or equal chance of being placed in a control group or an experimental group.
In experimental research, random assignment is a way of placing participants from your sample into different treatment groups using randomization. With simple random assignment, every member of the sample has a known or equal chance of being placed in a control group or an experimental group.